Breast cancer may be a metastatic tumor that arises inside the tissues of the breast. It is the most common cause of death in middle-aged women in western countries. All breast cancer can affect anyone. Women are at greater risk than men. Typically, the cancer forms in either the lobules or the ducts of the breast. Cancer also can occur within the fat or the fibrous animal tissue inside your breast.
The most serious and dangerous carcinomas are the metastatic carcinomas. It means that cancer has the ability to spread from place where it started into the tissues distant from the original tumor site. The commonplace for breast cancer to metastasize is into lymph nodes, under the arms or above the collarbone on the same side as cancer. Other common sites include- brain, the bones, liver. Cancers that have spread only into the lymph nodes under the arms are still curable, but those that metastasize in distant organs can extend the treatment for years.
The risk of breast cancer is due to a combination of factors. Having a risk issue does not mean you will get the malady, and not all risk factors have the same effect. Most women have some risk factors, however, most girls don’t get the carcinoma.
Here are some of the most common risk factors for breast cancer:
- Geographical: it occurs commonly in the Western world, accounting for three to five-person deaths.
- Age: carcinoma of the breast is extremely rare below the age of 20 years, but thereafter, the incidence steadily rises so that the age of 90 years nearly 20% of women are affected.
- Gender: but 0.5 % of patients with breast cancer are male.
- Genetic: women’s risk of breast carcinoma is higher with a family history of breast cancer than in the general population. Having a first-degree male relative with breast cancer also raises a woman’s cancer.
- Diet: because breast cancer so commonly affects women in the developed world, dietary factors may play a part in its causation. There is some evidence that there is a link between diets low in phytoestrogens. High intake of alcohol is also associated with an increased risk of developing carcinoma of the breast.
- History of radiation: women who had radiation therapy to the chest or breast before the age of 30 have a higher risk of getting breast cancer later in life.
- Reproductive history: having the first pregnancy after the age of 30, not breastfeeding and never having a full-term pregnancy can raise chances of the carcinoma of the breast.
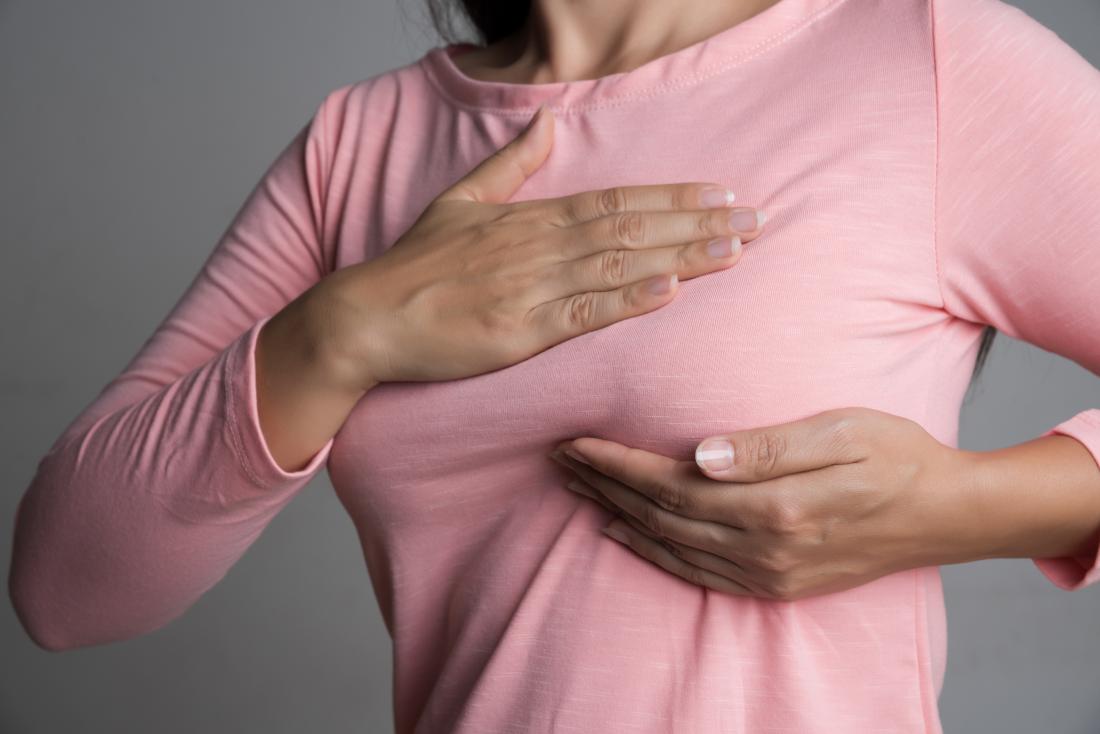 Although any portion of the breast, including the axillary tail, may be involved, breast cancer is found most frequently in the upper outer quadrant. Most breast cancer will present as hard lump, which may be associated with in drawing of the nipple. Early-stage breast cancer does not cause any symptoms or sign. Breast carcinoma is usually not painful. Most people discover breast cancer before symptoms appear, abnormality by finding and abnormality on mammogram or feeling a breast lump. Each sort of carcinoma can cause a spread of symptoms. Mainly of the symptoms are similar, but some can be different. The real breast cancer is diagnosed, the better the chance of successful treatment. So, it’s important to check your breast regularly. There are many different signs and symptoms of breast carcinoma, so checking your breast for any unusual change is important. here are some of the most common signs and symptoms of breast cancer-
Although any portion of the breast, including the axillary tail, may be involved, breast cancer is found most frequently in the upper outer quadrant. Most breast cancer will present as hard lump, which may be associated with in drawing of the nipple. Early-stage breast cancer does not cause any symptoms or sign. Breast carcinoma is usually not painful. Most people discover breast cancer before symptoms appear, abnormality by finding and abnormality on mammogram or feeling a breast lump. Each sort of carcinoma can cause a spread of symptoms. Mainly of the symptoms are similar, but some can be different. The real breast cancer is diagnosed, the better the chance of successful treatment. So, it’s important to check your breast regularly. There are many different signs and symptoms of breast carcinoma, so checking your breast for any unusual change is important. here are some of the most common signs and symptoms of breast cancer-
- Lump in the breast: Breast lump or tissue thickening that feels different it then surrounding tissue and has developed recently. It is usually seen in the chest or armpit region. You might feel the lump, but not see it in the initial stages. This lamp might also be gradually increasing in size.
- Discharge: Breast discharge is a common problem. Discharge is most concerning if it’s only from one breast or if it is bloody or any unusual discharge from either nipple. In any case, the doctor should evaluate all breast discharge.
- Skin texture: Change in the skin of the breast include- redness, change in skin texture- puckering or dimpling of the skin. Skin diseases usually cause their changes but occasionally can be associated with breast carcinoma.
- Change in nipple: Nipple inversion is a common variant of normal nipple, but nipple inversion that is new development needs to be of concern. Other changes in the nipple may include- rash, crusting of nipples.
- Change in color of the breast: An early sign of breast carcinoma is discoloration of the breast. The small section may appear red or pink. The breast may be inflamed and you can also notice a rash on the skin around the nipple.
- Change in position of the nipple: Your nipple might be pulled in all looks different for example changed in its position or shape.
- Change in the breast: You may notice a sudden, can explain the change in the shape or size of your breast. Although it is potential for individuals to possess breast that are slightly completely different in the slightest degree, this spelling would cause an amendment from their usual breast size. The skin over the affected breast feels tight due to swelling.
- Change in lymph nodes: Lymph nodes are a small collection of immune system tissues that filters fluid and captive potentially harmful cells. If a cancer cell leaves the breast, the first place it travels is the underarm lymph nodes region on the same side as the affected breast. This can lead to swelling in this region. In addition to a swelling of lymph nodes in the armpit, a person may also notice them around the collarbone. These lymph nodes may be tender to touch.
- Breast pain: Carcinoma of the breast can cause changes in skin cells that can lead to feelings of pain, tenderness, and discomfort in the breast. Although breast cancer is often painless, it is important not to ignore any signs or symptoms that could be due to carcinoma of the breast. Some people may also describe the pain like burning sensation.
 All the symptoms can also have a non-cancer is an underlying cause. However, population with these symptoms should speak to the general practitioner in case test are necessary to check for both non- cancerous and cancerous condition.
All the symptoms can also have a non-cancer is an underlying cause. However, population with these symptoms should speak to the general practitioner in case test are necessary to check for both non- cancerous and cancerous condition.
Everyone’s breasts are totally different, so get to know how your breasts normally look and feel. That way, it is simple to spot anything unusual. When you get to know your breast, you might easily notice the change with age or different time of months. For example- your breasts might feel tender and lumpy around the time of your periods. You may also notice normal changes during pregnancy, when your breast may get bigger and feel tender or sore.
Screening can help find breast cancer easily. Screening of breast means checking a woman’s breast for cancer before there are signs and symptoms of the disease. All the breast cancer screening can’t prevent breast cancer, it can help find breast carcinoma early when it is easier to treat. Early detection remains the primary way to prevent the development of the condition.
Imaging study used in breast carcinoma screening includes the following:
- Mammography
- Ultrasonography
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Women of age 40 to 44 years are recommended to have annual breast cancer screening with mammograms. Women age forty-five to fifty-four ought to get mammograms every year. Women 55 and older should switch to mammograms every 2 years or can continue early screening.
However, it is not forever doable to inform from these imaging tests whether or not a benign or cancerous. A breast biopsy is performed to remove some cells from the affected area in the breast and study them microscopically to determine a diagnosis. This procedure is also named as fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC). FNAC is considered as a good first-line method for investigating the cases of the breast carcinoma.
The stage of your breast cancer is an important factor in making decisions about your treatment. Most women with breast carcinoma in stages 1, 2, 3 are treated with surgery, often followed by radiation therapy. Women with breast carcinoma in stage 1 and 2 are most likely to get some kind of drug therapy which may include- chemotherapy, hormone therapy, HER2 targeted drugs or combination of these. Stage 3 cancer is treated with surgery first. Surgery is usually followed by adjuvant chemotherapy, hormone therapy. Radiation is recommended after surgery. Stage 4 breast carcinoma is a different ball game because the cancer is deemed to be metastatic. It may cause different symptoms depending on the body organ affected. Treatment for stage 4 breast cancer can include- surgery radiation and chemotherapy along with treating all the painful and uncomfortable symptoms to help a person have a better quality of life.
Most women will survive breast cancer if it is found and treated early. When breast cancer is detected early and is in a localized stage, the five-year relative survival rate is 100%. So take control of your health by playing routine breast self-exams, establishing current communication along with your doctor, obtaining associate degree annual clinical breast examination and programming your routine screening mammograms.







